If you own a website/blog or any product that has advertisements live on page it is suggested that you understand what Header Bidding is and how programmatic ad buying works. When HB (Header Bidding) was first launched it gained traction right away and became widely used and accepted as an industry standard. In 2018 more than half of United States websites have adopted header bidding as their main programmatic process. Yet, when asked people mostly understand very little about how header bidding or server side header bidding works. We believe that HB is the most important ad tech advancement since real time bidding (RTB) was first launched.
What is Header Bidding?
In order to understand what is server side header bidding first we need to understand how normally Header Bidding (also called as client-side wrapper) works. Here one header bidding partner acts as the container for all of the partners. Or it is created by using open source projects such as Prebid.js and Pubfood.js.
The buying process happens in the browser by collecting multiple bids from connected ad exchanges and SSP’s (supply-side platform). It is usually set up outside the publisher primary ad server. Therefore allowing advertisers to choose and pick the best impressions at the highest priority. This is also called as “first look”. Header bidding happens in the header of the page and is usually loaded before anything else appears on the page.
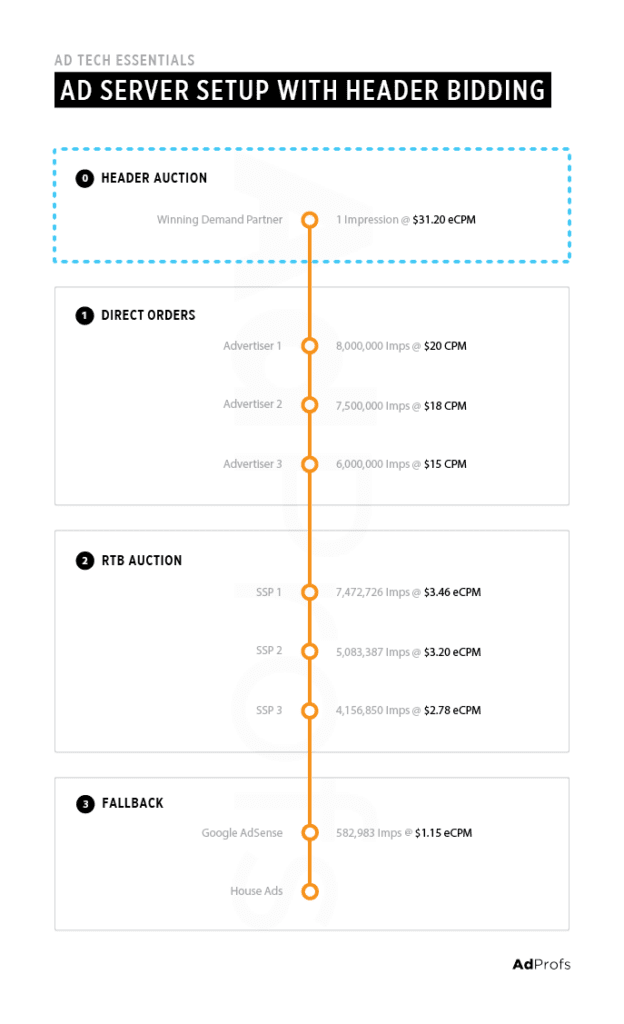
For sophisticated ad savvy websites they usually sell first impressions to Header Auction (with minimum bid applied). Then they pass the bid down to their Direct Orders (house campaigns). Then the leftover inventory is usually filled with self promoting campaigns.

How Client Side Header Bidding Works?
Step by step on how client side Header Bidding works:
- A visitor opens a web browser and enters the page URL.
- Web browser begins to load the page.
- The header bidding tag located in between the banner tags executes and then sends a request to the wrapper.
- Everyone starts to bid for the banners.
- The highest bid is recognised and is passed to the ad server.
- If the publisher has direct deals then the highest bid from header bidding is let to compete. (The best setup, but not many publishers use this)
- If there are no direct deals, then the winning advertisement is displayed.
- The ad server selects the highest eCPM bid and the ad is displayed.
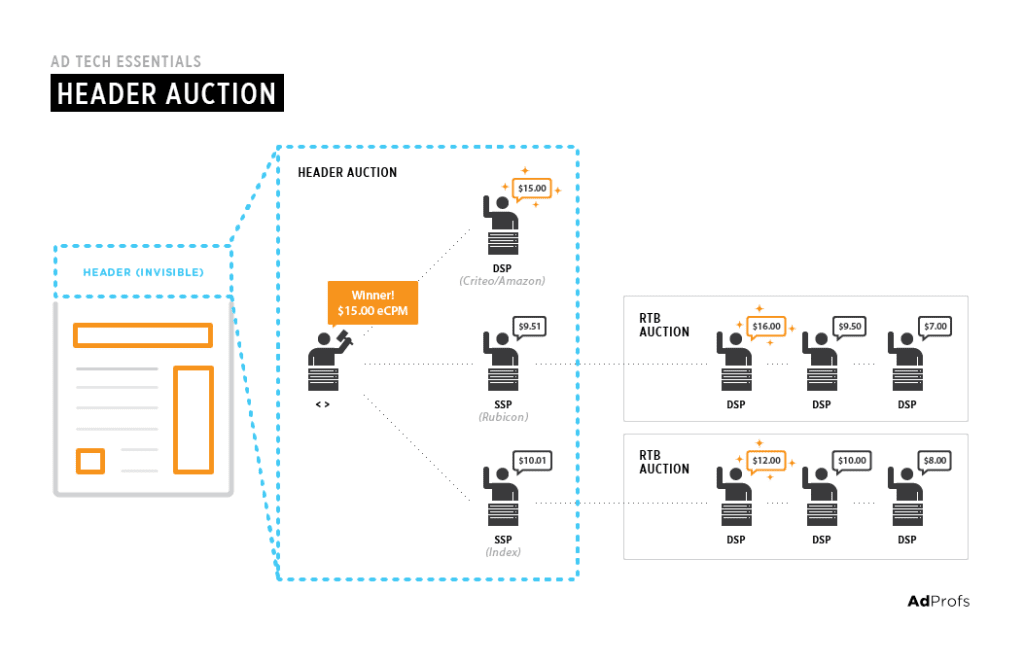

Header bidding takes some time to load. For this reason many publishers choose to apply a timeout 400-800 ms on desktop, 800 – 1200 ms on mobile. If the HB partner is not able to send their bid fast enough it does not get a chance to compete. This therefore pushes everyone to respond quickly and making the ads to load quickly and not slowing down the website. In the example of Image 2. we can see that in RTB auction where DSP’s make bids the highest is selected and this is called first price auction. Whereas some other SSP’s still use a second price auction meaning that the winning bid is second highest plus $0.01 – learn more about this here.
What is Server Side Header Bidding?
Now that we understand what client-side Header bidding is we can dive deep into Server Side Header Bidding (SSHB). SSHB is also called as server-to-server header bidding. Here, the auction takes place in the server instead of user web browser. The main reason for creating such a solution was to decrease the latency of header bidding, once the ad is sold it is displayed without affecting the page load time. The server side approach essentially creates unlimited scalability without any price on latency.
- A visitor opens a web browser and enters the page URL.
- Web browser begins to load the page.
- The header bidding tag located in between the banner tags executes and then sends a request to the external server (usually in cloud).
- Everyone starts to bid for the banners.
- The highest bid is recognised and is passed to the publisher ad server or the ad is displayed – if there are no direct deals.
- If the publisher has direct deals then the highest bid from header bidding is let to compete. (The best setup, but not many publishers use this)
- The ad server selects the highest eCPM bid and the ad is displayed.
What is the difference between server-side and client-side wrappers?
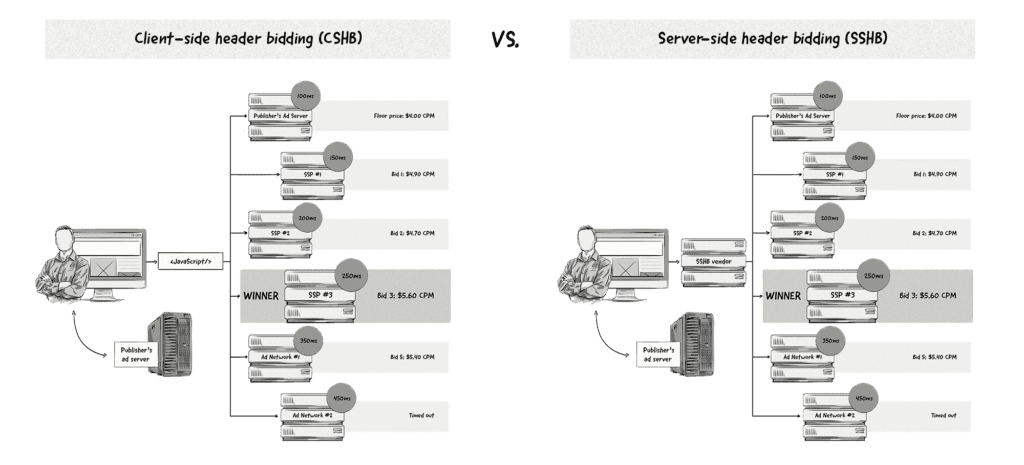

The main difference between the two types of header bidding is that in client side HB a publisher wrapper will call multiple ad exchanges in the visitor browser. Server side HB will make a call to an external server using the web browser. Therefore making all of the necessary calls to partners and ad exchanges.
Is Server Side Bidding Better?
Well, it has many drawbacks as well as many advantages over the client side header bidding. While one is better than other it mostly depends on how big of traffic the website has and is it really worth the time to invest. Here we go into general advantages and disadvantages of server side HB.
Advantages
The main differentiator is that browsers have request limitation, meaning that client side header bidding can only have a certain amount of ad requests during a session. Whereas for server side header bidding there is no limitation as the bids happen in the ad server instead of the browser.
As mentioned earlier the bidding happens in the server instead of web browser which leads to reduced latency and faster page loads. This leads to more opportunities, for example video header bidding. In client side HB it would just take too much time and would cause too much damage because videos are rich media and can delay website speed and increase the load.
Disadvantages
In client side header bidding you as a publisher would have a lot more control over choosing which partners to use and what floor-prices to apply. Therefore in server side header bidding is less transparent and the auction process remains hidden.
Most of the user data is filtered by the server which means that advertisers have less direct access to visitor cookies therefore some buyers might choose to not buy advertisement space “blindly”. Therefore giving advertisers less transparency. Server-side bidding is still a new technique and is to be accepted by the industry.
Should You Use Client Sider Server Bidding?
Ideally a publisher would need to test which works best with what partners. Generate some data and compare the results so that the best type of header bidding can be applied. It is also possible that a hybrid would work best, a lot of it depends on the publisher and the setup that is already in place.